Log in
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
Please note that ICA-AtoM is no longer actively supported by Artefactual Systems.
Visit https://www.accesstomemory.org for information about AtoM, the currently supported version.
Main Page > User manual > Getting started > Log in
To add or edit content in ICA-AtoM, you need to log in:
- Click the log in link in the user menu in the upper right-hand corner of the page. ICA-AtoM routes you to the log in page
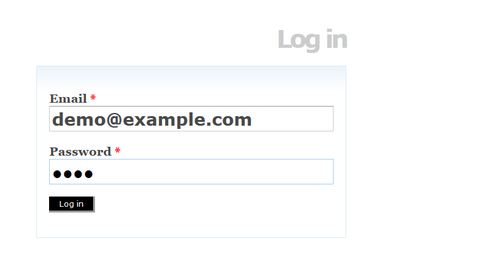
- Enter your email address
- Enter your password
- Click the log in button
- To log out, click the log out link in the user menu, ICA-AtoM returns you to the home page (view-only access)
- Note that ICA-AtoM automatically logs you out after thirty minutes of inactivity. To resume editing, you will have to log back in
New Login Security Features in ICA-AtoM 1.3!
If you are running the latest release of ICA-AtoM (version 1.3, available here ), administrators now have the ability to:
- force users to create strong passwords (using a mix of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols),
- force all authenticated user requests to use secure network communication ( Wiki page for https), and
- limit incoming requests for all Administrator functionality to a static IP range.
By default, these settings are turned off, and must be turned on by an administrator in Administer > Settings > Security.
- For more information on using these new login security features, please see the Administer > Settings > Security page of the User Manual.
- See, Security Documentation for more information about ICA-AtoM:
- Web application (AtoM) security
- Client-side (web browser) security
- Server-side security