Difference between revisions of "Edit permissions"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
*Note that users belonging to the contributor group do not automatically inherit the ability to create, update and delete taxonomy terms. You can change these permissions for either the contributor group or an individual user. In this case, we will add the ability to create, update and delete subject terms to our individual user. | *Note that users belonging to the contributor group do not automatically inherit the ability to create, update and delete taxonomy terms. You can change these permissions for either the contributor group or an individual user. In this case, we will add the ability to create, update and delete subject terms to our individual user. | ||
| − | Steps: Go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. Click on Taxonomy permissions (next to Authority record permissions). Click Edit. Click Permissions by taxonomy, then click Add taxonomy. Select Subjects as the taxonomy name from the auto-complete list. Next to Create, Update and Delete select Grant, then save the record. The user should now be able to create, update and delete subject terms but not other kinds of taxonomy terms. | + | Steps: Go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. Click on Taxonomy permissions (next to Authority record permissions). Click Edit. Click the blue link "Permissions by taxonomy", then click "Add taxonomy". Select Subjects as the taxonomy name from the auto-complete list. Next to Create, Update and Delete select Grant, then save the record. The user should now be able to create, update and delete subject terms but not other kinds of taxonomy terms. |
Revision as of 12:09, 9 April 2010
Please note that ICA-AtoM is no longer actively supported by Artefactual Systems.
Visit https://www.accesstomemory.org for information about AtoM, the currently supported version.
Main Page > User manual > UM-7 Administer ICA-AtoM > UM-7.2 1.0.9 Edit user permissions in ICA-AtoM 1.0.9
When refining user permissions, it is often useful to start with the group to which the user belongs. You can refine permissions for the group, then add users to the group, all of whom will inherit the modified permissions. To lean how to refine user permissions, follow the steps in scenario 1, below. Then try some more of the scenarios listed at the bottom of this page, all of which relate to the user created in scenario 1.
- You should have two or more archival institutions in your system, with several hierarchical descriptions attached and some digital objects uploaded, in order to fully test the scenarios on this page.
- You can only modify the user's settings if you are logged in as an administrator. After completing the steps in each scenario, log out and log back in as the user you've been creating and modifying in order to see the results of your modifications.
Scenario 1: In a multi-repository system, add a user who can create, update and publish archival descriptions belonging to one archival institution only.
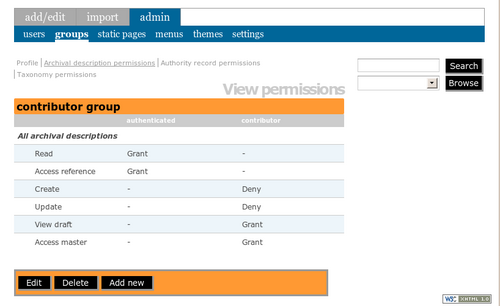
In the main menu bar, go to admin > groups > contributor. Click on Archival description permissions in the grey menu above the title bar. Your screen will show the default "Grant" permissions for the contributor group - i.e. it shows you everything the user is permitted to do (see fig.1).
- Note that the contributor group inherits some of its settings from its parent group, authenticated (which is all users who have successfully logged-in).
- Any permission that has not been "granted" by the current group (contributor) or it's parent group (authenticated) is considered "denied" by default. In other words the default for the system is to deny permission (default deny) unless a rule explicitly grants it.
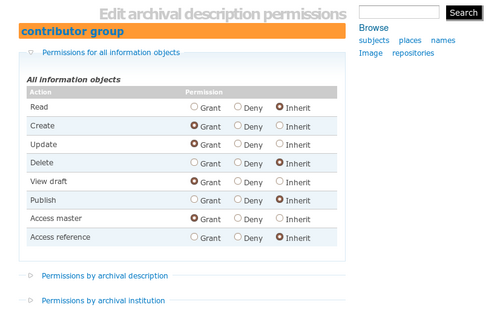
Click Edit. In the edit screen, you will get a better sense of the group's permission settings (see fig.2) . The contributor has the following permissions:
- Read: Grant (inherited from authenticated group)
- Create: Grant
- Update: Grant
- Delete: Deny (default deny)
- View draft: Grant
- Publish: Deny (default deny)
- Access master digital object: Grant
- Access reference digital object: Grant (inherited from authenticated group).
- In other words, any user belonging to the contributor group automatically has been granted the ability to read, create and update descriptions, view draft descriptions and access digital objects. However, the user has been denied the ability to delete or publish descriptions. In this Scenario 1, we would like to create a user who can create and update descriptions belonging only to a particular institution and can also publish archival descriptions belonging to the institution.
In order to restrict permissions to descriptions of a particular institution, we need to first deny the permissions to all contributors, and then add them back for the specified institution. We will do the blanket denials in the contributor group edit screen, and later add a user with permissions granted for a particular institution. To deny the permissions in the contributor group, open the edit screen and select Deny for the Create and Update permissions (See fig.3).
Click Save. Your show screen should look like the screen in fig.4.
Go to admin > users and add a new user as shown in fig. 5. Be sure to add the user to the contributor group. Click create when you're done entering the data.
Click on Archival description permissions. You will see the permissions that are specified in the contributor group, as in Fig.6.
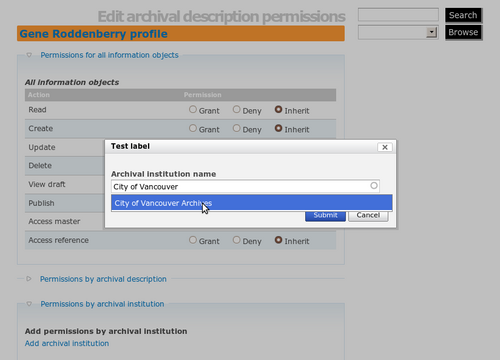
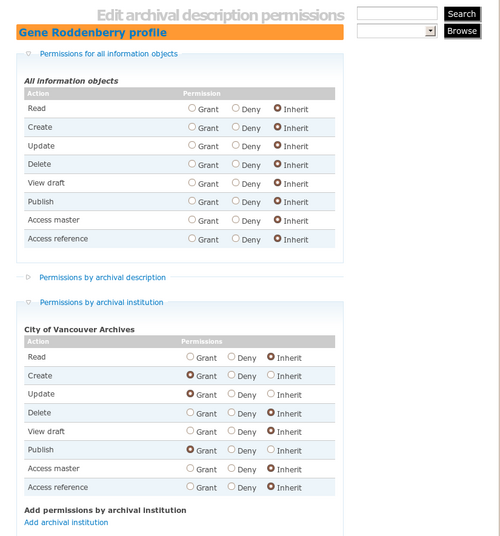
Click Edit. Click on the blue ""Permissions by archival institution" link and then the "Add archival institution" link. Select the archival institution as in fig.7.
You will now be able to add permissions specific to descriptions belonging to this archival institution. For Create, Update and Publish, select Grant as in fig.8.
Save the record. The screen should show the modified permissions as in fig.9. To test your permissions, try logging out and logging back in as the user you created. You should be able to create, edit and publish descriptions belonging to the specified institution only, and you should not be able to delete any descriptions.
Scenario 2: Add the ability to delete the archival descriptions of the specified institution.
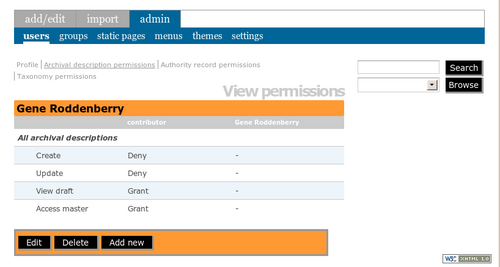
Steps: Remember that a user in the contributor group does not automatically have the ability to delete any records. To add the ability to delete archival descriptions belonging to the archival institution the user can currently edit and update, go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. Click Archival description permissions. Click Edit. For the specified institution, change the Delete permission to Grant.
Scenario 3: Remove the ability to create and update authority records.
- Permissions for authority records can be refined in some of the same ways they can be refined for archival descriptions. In a multi-repository setting it may be desirable to prevent users from creating and/or updating authority records, because one authority record may be linked to archival descriptions belonging to more than one archival institution.
- Note that users belonging to the contributor group automatically inherit the ability to create and update authority records.
Steps: Go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. Instead of clicking on Archival description permissions, click on Authority record permissions. Click Edit. Under All authority records, next to Create and Update, select Deny, then save the record.
Scenario 4: Add the ability to translate to a specified language.
There are two ways to grant translate permissions to non-administrators:
- Make the user a translator by adding him to the translator group (the same way that you made Gene Roddenberry a contributor). This means that he will be able to translate to any language.
- Instead of making the user a translator, which would allow him to translate to any language, add a language to which a user can translate. This means that he will be able to translate only to the specified language, and only those archival descriptions and authority records he is allowed to update. In this scenario, we will add the ability of the user to translate to Dutch.
Steps: Go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. You should be in looking at the View user profile screen; if not, click Profile (to the left of Archival description permissions). Click Edit, then click on the blue "Access control" link. In allowed languages for translation, select Dutch. click Save. The user will now be able to translate from any source language to Dutch. Note that the list of languages is derived from the languages added in the settings menu. See UM-7.4.5 Add or remove a language. Note also that you can add more languages from this list as needed.
Scenario 5: Remove the ability to view and download digital master objects.
- Note that users belonging to the contributor group automatically inherit the ability to view and download master digital objects.
Steps: Go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. Click on Archival description permissions. Click Edit. Under All archival descriptions next to Access master click Deny. Save the record. This will allow the user to view thumbnail and reference display copies of digital objects, but not to view or download the master objects. Note that if you do not wish to have any users belonging to the Contributor group viewing or downloading masters digital objects, deny permission for this activity at the level of the group - i.e. go to admin > groups > contributor and make the change at that level instead of the level of the individual user.
Scenario 6: Add ability to create, update and delete subject terms.
- Note that users belonging to the contributor group do not automatically inherit the ability to create, update and delete taxonomy terms. You can change these permissions for either the contributor group or an individual user. In this case, we will add the ability to create, update and delete subject terms to our individual user.
Steps: Go to admin > users > Gene Roddenberry. Click on Taxonomy permissions (next to Authority record permissions). Click Edit. Click the blue link "Permissions by taxonomy", then click "Add taxonomy". Select Subjects as the taxonomy name from the auto-complete list. Next to Create, Update and Delete select Grant, then save the record. The user should now be able to create, update and delete subject terms but not other kinds of taxonomy terms.