Difference between revisions of "Entity types"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| − | + | An [[Entity|entity]] is an object about which an information system collects data. ICA-AtoM's architecture include a number of [[Entity|entity]] types, but from the user's point of view there are four main types with which they will interact: | |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Archival description|Archival descriptions]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Authority record|Authority records (actors)]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Archival institution|Archival institutions]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Term|Terms]] |
Revision as of 11:26, 14 April 2009
Please note that ICA-AtoM is no longer actively supported by Artefactual Systems.
Visit https://www.accesstomemory.org for information about AtoM, the currently supported version.
Entity types
Main Page > (UM) User manual > UM-1 System overview > UM-1.3 Entity types
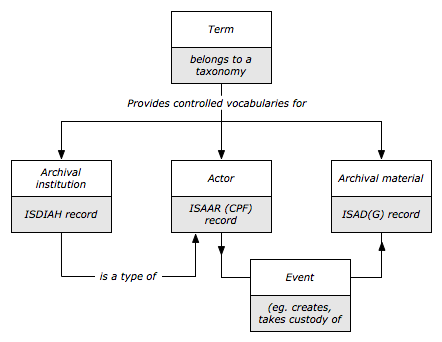
An entity is an object about which an information system collects data. ICA-AtoM's architecture include a number of entity types, but from the user's point of view there are four main types with which they will interact:
Archival descriptions
- Provide contextual information about archival materials.
- Are aranged into hierarchical levels (fonds, series, files, items).
- Include data elements based on the ICA's General International Standard Archival Description (ISAD-G).
Authority records (actors)
- Provide descriptions of the actors (corporate bodies, persons and families) that interact with archival materials as creators, custodians, subject access points, etc.
- Include data elements based on the ICA's International Standard Archival Authority Records (Corporate bodies, Persons, Families) (ISAAR(CPF)).
- Are linked to archival descriptions in ICA-AtoM by events delimited by start / end dates. Through events, 1 actor can have 0, 1 or many relationships to 0, 1 or many archival units; and 1 archival unit can have 0, 1 or many relationships to 0, 1 or many actors. Event relationships link ISAAR authority files (descriptions of actors) and ISAD records (descriptions of archival materials).
Archival institutions
- Provide descriptions of repositories that preserve and provide access to archival materials.
- Include data elements based on the ICA's International Standard for Describing Institutions with Archival Holdings (ISDIAH).
- Are actors that hold archival materials. Like all actors, an archival institution has its own ISAAR authority record. But its characteristics as a repository (e.g. its opening hours, research services, contact information) are described separately in an ISDIAH institution record. The ISDIAH elements that are inherited from its ISAAR authority record are: Authorized form of name, Other forms of name, Parallel forms of name, History, Mandates/Sources of Authority, and Administrative structure.
Terms
- Provide controlled vocabularies used throughout the system (e.g. as access points or in drop-down value lists).
- Are organized into separate taxonomies.
- Include minimal data elements; a future iteration of ICA-AtoM will extend one such taxonomy ("Function description") to include the elements found in the ICA's International Standard For Describing Functions (ISDF).