Difference between revisions of "Entity types"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== Functions == | == Functions == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Provide a means of describing the activities of records creators and other actors linked to records creation and maintenance | ||
| + | * Analysis of the functions of corporate bodies is important as the basis for many recordkeeping activities. Functions are recognised as generally being more stable than administrative structures, which are often amalgamated or devolved when restructuring takes place. Functions are therefore well suited to act as: | ||
| + | ** a basis for the arrangement, classification and description of records | ||
| + | ** a basis for the appraisal of records | ||
| + | ** a tool for the retrieval and analysis of records. | ||
| + | * In ICA-AtoM functions are based on linked to [[Glossary#Authority record|authority records]] and to other functions. | ||
Revision as of 11:42, 31 May 2010
Please note that ICA-AtoM is no longer actively supported by Artefactual Systems.
Visit https://www.accesstomemory.org for information about AtoM, the currently supported version.
Main Page > User manual > UM-1 System overview > UM-1.3 Entity types
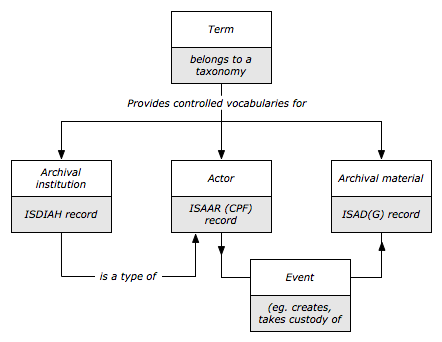
An entity is an object about which an information system collects data. ICA-AtoM's architecture includes a number of entity types, but from a user's point of view there are four main types with which they will interact:
Archival descriptions
- Provide contextual information about archival materials
- Are arranged into hierarchical levels (fonds, series, files, items)
- Include data elements based on the ICA's General International Standard Archival Description (ISAD(G))
Authority records
- Provide descriptions of the actors (corporate bodies, persons, and families) that interact with archival materials as creators, custodians, subject access points, etc.
- Include data elements based on the ICA's International Standard Archival Authority Records (Corporate bodies, Persons, Families) (ISAAR(CPF))
- Are linked to archival descriptions in ICA-AtoM by events delimited by start/end dates. Through events, one actor can have zero, one, or many relationships to zero, one, or many archival units; and one archival unit can have zero, one, or many relationships to zero, one, or many actors. Event relationships link ISAAR authority files (descriptions of actors) and ISAD records (descriptions of archival materials)
Archival institutions
- Provide descriptions of repositories that preserve and provide access to archival materials
- Include data elements based on the ICA's International Standard for Describing Institutions with Archival Holdings (ISDIAH)
- Are actors that hold archival materials. Like all actors, an archival institution has its own ISAAR authority record. But its characteristics as a repository (e.g. its opening hours, research services, contact information) are described separately in an ISDIAH institution record. The ISDIAH elements that are inherited from its ISAAR authority record are: authorized form of name, other forms of name, parallel forms of name, history, mandates/sources of authority, and administrative structure
Functions
- Provide a means of describing the activities of records creators and other actors linked to records creation and maintenance
- Analysis of the functions of corporate bodies is important as the basis for many recordkeeping activities. Functions are recognised as generally being more stable than administrative structures, which are often amalgamated or devolved when restructuring takes place. Functions are therefore well suited to act as:
- a basis for the arrangement, classification and description of records
- a basis for the appraisal of records
- a tool for the retrieval and analysis of records.
- In ICA-AtoM functions are based on linked to authority records and to other functions.
Terms
- Provide controlled vocabularies used throughout the system (e.g. as access points or in drop down value lists)
- Are organized into separate taxonomies
- Include minimal data elements; a future iteration of ICA-AtoM will extend one such taxonomy (function description) to include the elements found in the ICA's International Standard For Describing Functions (ISDF)